Sampling is a common method for researchers to take a sample of the total object and gain insight of the total by studying that sample.
In the realm of research practice, sampling requires consideration of two aspects: sampling protocol and execution procedure. Based on the research requirements, practitioners typically opt for systematic sampling or stratified random sampling for textual content to establish a codified sample library suitable for manipulation. The specific choice of sampling protocol varies according to the distinct research context.
In the realm of operational procedures, the DiVoMiner platform offers a seamless sampling method, encompassing a total of three steps: establishing the sampling pool, defining the sampling protocol, executing the sampling. Strictly speaking, user intervention is only required for the first two steps. The specific method is to access to the [Overview] page and clicking on [Sampling] under the relevant database, whereupon a pop-up will display the steps for the sampling process.
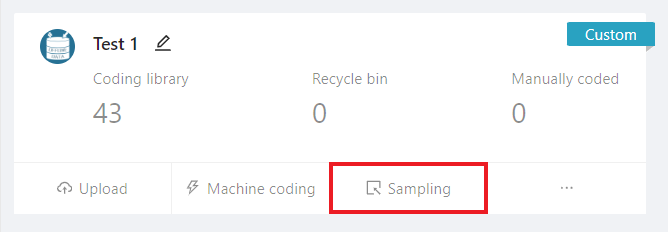
After clicking [Sampling], if there is no existing sampling pool, create a new one and name it, then click “Next”.
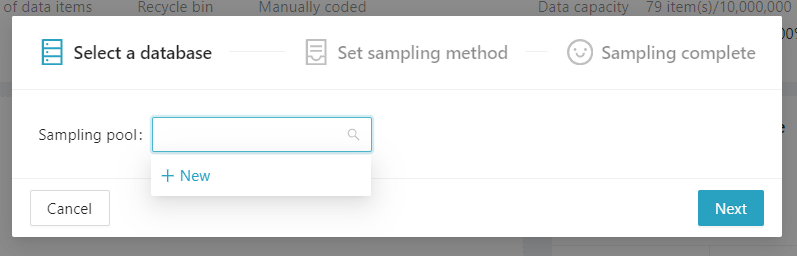
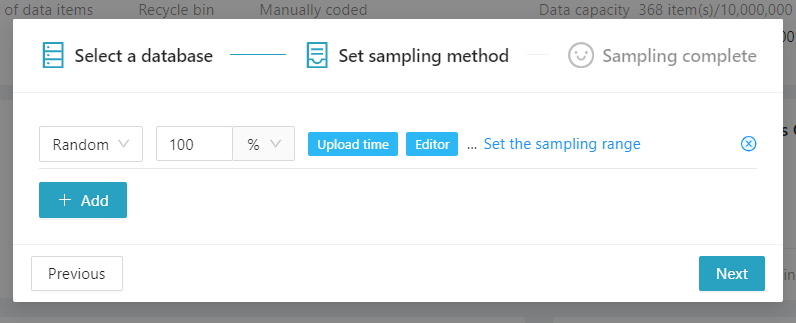
Enter the [Set sampling method] to set the sampling rules. If the sample only has to be extracted randomly, you can simply enter the percentage of data to be randomly selected or a specific amount of data, and click [Next].
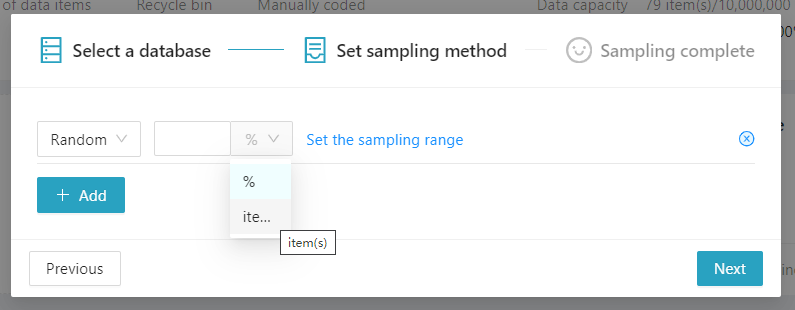
However, during practical textual analysis, more complex sampling requirements often arise. For instance, there may be a need to prioritize popular tweets from a dataset for manual analysis. In such cases, clicking on [Set the Sampling Range] allows for the personalization of sampling rules.
Then, after clicking [Set the Sampling Range], establish the sampling conditions and rules. Click on the “+” or “-” symbols to add or remove the conditions. The rule can be set to fulfill either [All the conditions] or [Any condition]. In the example below, five conditions have been set, employing “all conditions,” which means that only data satisfying all five conditions will be selected as samples.
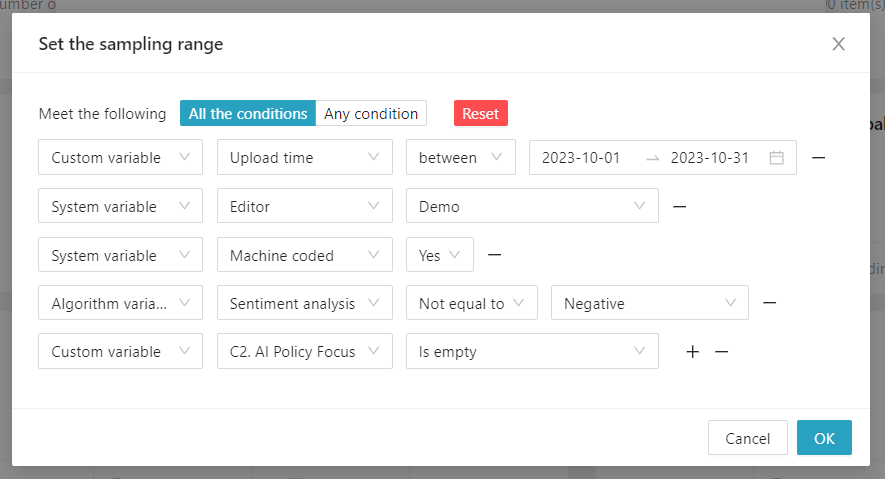
Users have the liberty to freely select these conditions. Once the conditions are set, clicking “OK” will return to the [Set sampling method] page, where adjustments to the sampling fields and rules can be made. For instance, sampling can be conducted in ascending or descending order based on criteria such as likes, comments, shares, and others.
In this example, 100% random sampling was chosen, indicating that all data meeting the conditions will be included. After that, click on “Next” to initiate the sampling process. Apart from random sampling, users can also select sampling in ascending or descending order.
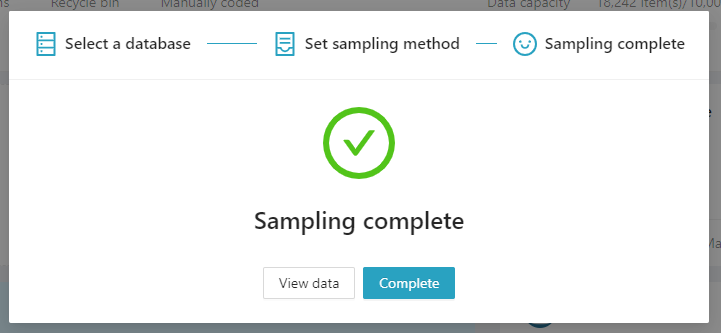
Just wait for a moment and the sampling is complete. Click [View Data], you can see the eligible data drawn according to the conditions. Please be reminded that after sampling, an independent database will be formed, which can be operated separately and in parallel with multiple databases. However, the sampling pool is taking up the topic data capacity and file capacity—thus, please plan your project usage wisely.
