With keywords, you can search for related content results in a large quantity of data. In the research process, it happens often to repeatedly adjust the keyword setting in order to obtain more comprehensive and representative analysis results.
The role of keywords is significant in both manual coding scenarios and machine coding scenarios. In a manual coding setting, keywords help highlight and preselect options in the coded text. In a machine coding setting, keywords serve as the logical basis for machine judgment. By setting up keywords, the coding process can involve AI-aided coding and machine coding.
Note: There are certain formatting requirements that need to be followed when setting up keywords:
- Parentheses (), quotation marks “”, etc. should appear in pairs and with English formatting;
- Boolean Operators such as AND/OR/NOT should be included. Space is required before and after each Boolean Operator. After successful input, the Boolean Operators will be shown in black and the keywords will be red;
- Keywords are case-insensitive in English, meaning that the capitalization of letters does not affect their recognition. Similarly, keywords in Chinese can be written in either simplified or traditional characters without effecting their recognition;
- Boolean Operators need to be capitalized;
- When keywords consist of English phrases or a mixture of multiple languages, it is recommended to enclose each keyword phrase in double quotation marks to ensure accurate machine recognition;
- For keywords in numeric format, enclose them in double quotation marks.
- To retrieve two characters between a certain number of words, the keyword rule would be “A B”~value. For example, [“Sinovac Vaccine”~10] means searching for content within 10 characters that contain both the keywords “Sinovac” and “Vaccine”.
For example:
- To research a Project related to the Hong Kong-Zhuhai-Macao Bridge, keywords can be set as:
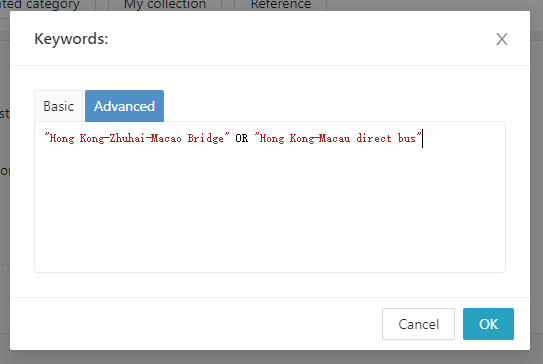
“Hong Kong-Zhuhai-Macao Bridge” OR “Hong Kong-Macau direct bus” means that the text with either phrase of “Hong Kong-Zhuhai-Macao Bridge” or “Hong Kong-Macau direct bus” are in the search range. Examples of search results text are shown as follow:
a) The completion of the Hong Kong-Zhuhai-Macao Bridge will reshape the urban space of the Pearl River Estuary.
b) The opening of the Hong Kong-Macau direct bus will greatly shorten the travel time between the three places of Hong Kong, Macau, and Zhuhai.
2. The above search criteria can be further optimized. For example, in the text, the term “Hong Kong-Zhuhai-Macao Bridge” may not appear all at once as a whole. In this situation, the keyword can be modified as follow:
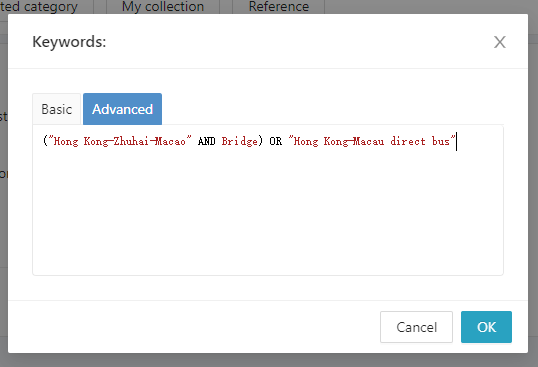
“Hong Kong-Zhuhai-Macao” AND “Bridge” means that the phrase “Hong Kong-Zhuhai-Macao” and the “Bridge” must both appear in the text at the same time, but do not need to appear as a whole. At this time, if either Condition 1 (Hong Kong-Zhuhai-Macau AND Bridge) or Condition 2 (Hong Kong-Macau direct bus) is true, the text will be in the search range. The example search results are shown as follow:
a) In order to enhance the Hong Kong-Zhuhai-Macao linkage, a bridge was built.
b) The Hong Kong-Macau direct bus greatly facilitates the travel between people in the two places.
- The search criteria allow for multi-level logical relationships.
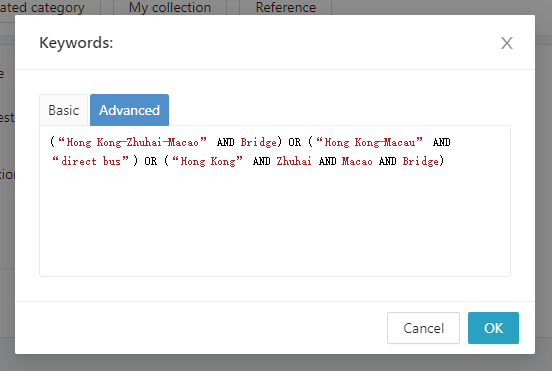
For example, when the keyword setting is “Hong Kong-Macau” AND “direct bus”, it indicates that the text should contain both keywords of “Hong Kong-Macau” and “direct bus”, while they do not need to appear consecutively. The following are examples of sentences that in the search scope:
a) The bridge spanning across the three regions of Hong Kong, Macau, and Zhuhai is known as the “Mount Everest of bridges”.
b) Direct buses operating 24 hours/day shuttle between Hong Kong and Macau.
c) The Hong Kong-Zhuhai-Macao Bridge has a trilateral enforcement mechanism.
